What is an Inverting Op Amp?
- An inverting op-amp (operational amplifier) is a circuit that gives an output voltage 180 degrees out of phase with the input voltage.
- The simple way to understand is, if the input pulse is positive, then the output pulse will be negative and vice versa.
- Now let’s understand the operation of the inverting amplifier below.
How do inverting op amps work?
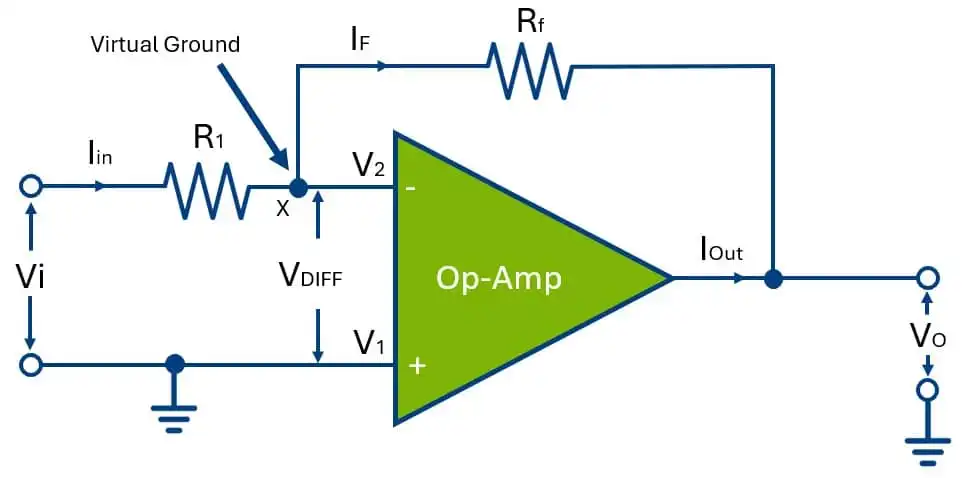
- Here is the input signal which is to be amplified is applied to the inverting (-) terminal through the resistor R1 of the Op-Amp.
- The other resistor is the feedback resistor (Rf) is connected between the output and inverting (-) pins of the op-amp.
- The non-inverting (+) terminal is connected to the ground.
- The detailed connection diagram of the inverting amplifier is shown in fig.
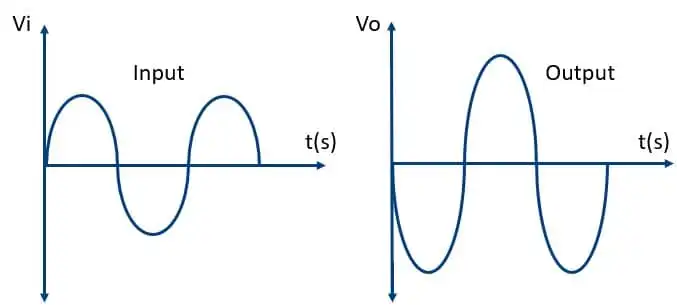
Inverting Op Amp Waveforms
- The input and output waveforms of the inverting op-amp are shown in the below figure.
- These waveforms are created by assuming that the amplifier’s gain and a sine wave are used as input signals.
- From these waveforms, it’s evident that the output is twice the size of the input, like Vout = Av * Vin, and its phase is opposite to the input.
Expression for close loop voltage gain (Avf):
As we know for the ideal Op-Amp Voltage gain Av= ∞ and Input Impedance Ri=0.
From the above figure, we can write that,
Vo = |Av| x Vi
From the above figure, we can write that,
Av=VoVi
Where,
Vi-V2 = IR1
V2-Vo = IRf
Because of op amp has input impedance is infinite, the currents flowing into its input terminals are zero i.e. I1 = I2 = 0. Thus, Ii = If. Hence,
So we can write
Vi-V2 = IR1
V2-Vo = IRf
Since the input resistance Ri=∞, the current going into the Op-Amp will be zero, therefore the current “I” that passes through R1 will also pass through Rf as shown in Fig, As voltage V2 = 0, the input voltage Vi is the voltage across R1 and the voltage across Rf is the output voltage.
The input voltage is given by,
Vi-0 = IR1
The output voltage is given by,
0-Vo = IRf
From, the above two equations, we get,
-VoVi= IRfIRi
VoVi=- RfRi
The final equation for the voltage gain of the inverting amplifier is,
Av = -Rf/R1
Advantages
- The two input terminals of this op-amp are always at zero (Virtual ground). Therefore, only the differential mode signal will be present.
- It operates using negative feedback.
- The gain factor is exceptionally high.
- The output of this op-amp is a out of phase with the input signal.
Disadvantages
- The output of this op-amp is out of phase with the input signal, which may not be suitable for certain applications.
- Inverting op-amps typically have a low input impedance (Equals to R1)
- In some cases, the inverting configuration may attenuate the input signal.
- Maintaining distortion-free feedback can be challenging, particularly at high gain levels.


xfthtryh